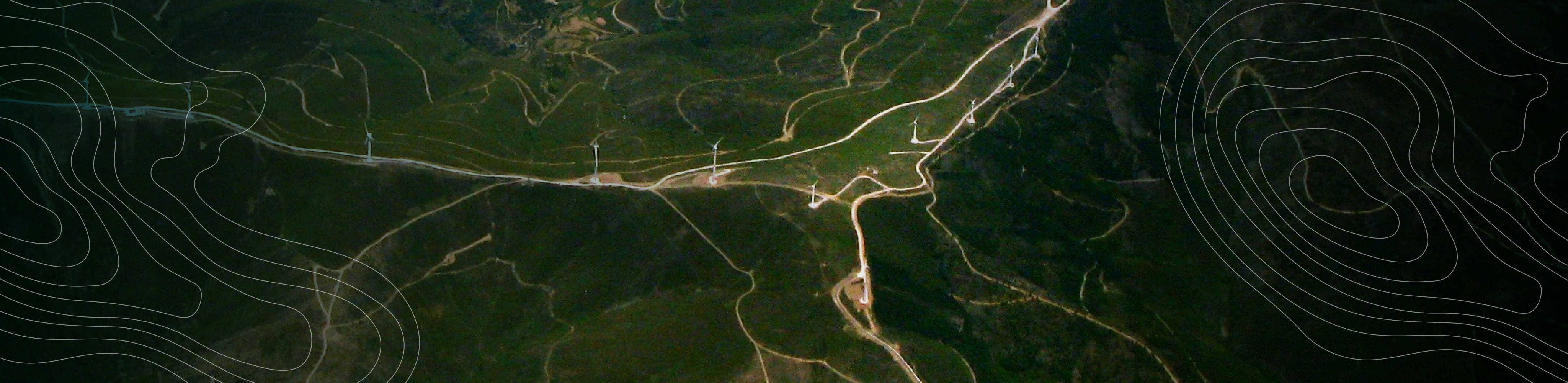
Defining the
Path to Net Zero
A
Afforestation
The planting of new trees to establish woods in locations that had previously been devoid of trees.
Article 6
Established during COP26, Article 6 sets the rules for crediting mechanisms to be used by the 193 signatories of the Paris Agreement to reach emission reduction targets or NDCs. The implementation of Article 6 has made it possible for countries to buy voluntary carbon credits.
B
Blue Carbon
Blue carbon is the carbon absorbed and deposited in biomass and sediments by living organisms in coastal and marine environments, such as mangroves, salt marshes, and seagrasses.
C
Carbon
Carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases (GHGs) that contribute to climate change.
Carbon Credit
A carbon credit is a transferable certificate issued by a carbon credit rating agency to represent an emission reduction of one metric tonne of CO2, or an equivalent amount of other greenhouse gases (GHGs).
Carbon Credit Delivery Date
The carbon credit delivery date is the date a carbon credit will be available for purchase on the market.
Carbon Credit Vintage
Refers to the year a carbon credit was issued. The vintage of an offset may not necessarily match the year of the transaction, and the vintage year may even be in the future.
Carbon Market
A marketplace that treats emissions reductions as a commodity, where participating members can buy and sell carbon credits.
Carbon Offset
A reduction or removal of emissions of CO2 or other GHGs made in order to compensate for emissions made elsewhere.
Carbon Sink
The most important carbon sink on the planet is the ocean. Any natural or man-made reservoir that collects and stores any carbon-containing chemical component for an indefinite length of time, lowering CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere.
Carbon Storage Asset
The physical structure or end product that carbon is stored in.
Climate Change
Defined by the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, climate change is, “A change of climate which is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and which is in addition to natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods.”
COP
COP stands for Conference of the Parties. In this sphere, the parties are the governments that have signed the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and includes over 190 countries. The COP brings these signatory governments together once a year, since 1995, to discuss how to jointly handle climate change.
COP26
The 2021 UN Climate Change Conference, referred to as COP26. Signatories agreed to cut climate pollution in half from current levels by 2030 and bring them down to net zero by 2050 to meet the Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C target.
E
ESG
Stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. These non-financial factors are considered increasingly integral to investment decisions as a means of identifying risks and growth opportunities. ESG is the fastest growing sector in finance today.
Emissions
The release of greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere.
G
Greenwashing
Using false or misleading marketing to exaggerate an organization’s environmental or sustainability activities.
GHGs
GHGs stands for greenhouse gases, which are gases that trap heat within the atmosphere. Common GHGs include methane, nitrous oxide, fluorinated gases, and carbon dioxide, which is one of the most recognizable GHGs and a primary contributor to global warming.
I
Issuing Registry
The body which oversaw the registration and verification of the project and which issues and monitors the carbon credits generated by the project. There are four major voluntary offset project registries—American Carbon Registry (ACR), Climate Action Reserve (CAR), Gold Standard, and Verra (VCS).
N
Net-Zero
A target of completely negating the amount of GHGs produced by human activity, to be achieved by reducing emissions and implementing methods of absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and sequestering carbon from the environment.
NDCs
NDC stands for Nationally Determined Contributions. Established by the Paris Agreement in 2015, NDCs refer to each participating country’s outlined efforts to reduce national emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change, in alignment with the Paris Agreement’s climate action goals.
P
Paris Agreement
The first legally binding global climate change agreement, adopted at the Paris climate conference (COP21) in December 2015. It sets out a global framework to avoid the negative effects of climate change by limiting global warming to 1.5°C.
Project
Any carbon emission reduction or removal activity that generates certified carbon credits and is shown in the declarations.
Project Owner
The operator and owner of the physical project installation where the emission reduction project takes place. An owner can be any private person, company or other organization.
Project Proponent
A person or organization with the intention to develop an emission reduction project. This could be the project owner, a consultant, or specialized services provider.
R
Retire
To permanently remove carbon credits from the market in order to prevent them from being resold after they’ve been used to their full capacity. Carbon credits are typically decommissioned by assigning them unique serial numbers and registering them in an official registry.
S
SEC Regulatory Compliance
SEC has established requirements for Climate Disclosures in 2024 Filings.
Sequestration
The capture, removal, and storage of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into a carbon pool. Sequestration can occur through biological (e.g., photosynthesis in plants and trees), chemical (e.g., turning CO2 into carbonate minerals), or physical processes (e.g., storage of carbon dioxide in underground reservoirs).
Nearly 350 million carbon credits were issued in 2021, representing a 220% increase in volume from 2020.
Source: sylvera.com
More Questions?
We have the answers.
 Carbon Protect™
Carbon Protect™


